Difference between revisions of "Smart contract"
(fchanged img upright x2) |
(added reference to Autonomous Agents) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
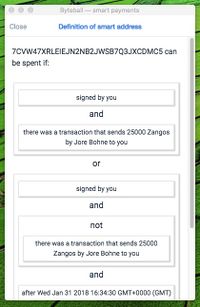
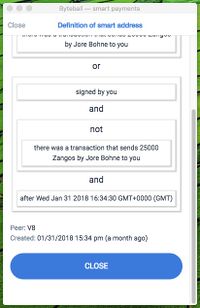
| − | [[File:smart-address-1.jpg|thumb|upright=0.65]][[File:smart-address-2.jpg|thumb|upright=0.65]]About smart contracts, the basis of conditional payments ("smart payments"), | + | [[File:smart-address-1.jpg|thumb|upright=0.65]][[File:smart-address-2.jpg|thumb|upright=0.65]]About smart contracts, the basis of conditional payments ("smart payments"), Obyte's killer feature. And "the competition". Not too technical. Compare to [[Prosaic contract]]s, and also [[Autonomous Agent]]s. |
==Contracts. Ethereum, right?== | ==Contracts. Ethereum, right?== | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Obyte''' does '''simple''', human-readable contracts to perform simple actions. |
'''Ethereum''' does '''complex''', programmer-readable contracts to perform complex actions. | '''Ethereum''' does '''complex''', programmer-readable contracts to perform complex actions. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===But Rootstock?=== | ===But Rootstock?=== | ||
| − | Rootstock is a centralized smart-contract platform planned to be layered on top of Bitcoin. RSK | + | Rootstock is a centralized smart-contract platform planned to be layered on top of Bitcoin. RSK was just released on Bitcoin testnet.<ref>https://www.reddit.com/r/Bitcoin/comments/6e7mdz/rsk_testnet_is_open/?st=j3bxt1g7&sh=63cbb552 Reddit thread 2017-05-30</ref> |
One post: RSK is EVM on BTC (that is, Ethereum Virtual Machine infrastructure, but linked to and secured by bitcoin's blockchain instead, using sidechains.) | One post: RSK is EVM on BTC (that is, Ethereum Virtual Machine infrastructure, but linked to and secured by bitcoin's blockchain instead, using sidechains.) | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Offering smart contracts== | ==Offering smart contracts== | ||
| − | When you want to create a new smart contract with a user, your sequence is usually as follows:<ref>https://github.com/byteball/byteballcore/wiki/Writing-chatbots-for-Byteball Github: Writing chatbots for | + | When you want to create a new smart contract with a user, your sequence is usually as follows:<ref>https://github.com/byteball/byteballcore/wiki/Writing-chatbots-for-Byteball Github: Writing chatbots for [Obyte]</ref> |
# You ask the user to send his payment address (it will be included in the contract) | # You ask the user to send his payment address (it will be included in the contract) | ||
# You define a new contract using the user's address and your address as parties of the contract | # You define a new contract using the user's address and your address as parties of the contract | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
See wiki [[Oracle]] article for examples and [[videos]]. | See wiki [[Oracle]] article for examples and [[videos]]. | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| + | ==Recovering smart contracts== | ||
| + | The contract is hidden once it is emptied but it still exists. To unhide it, you can send any coins, even 1 byte, to the contract address. | ||
| + | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | *[https://hackernoon.com/smart-contracts-ethereum-vs-obyte-72f95ab6bde7 Smart contracts: Ethereum vs. Obyte] | |
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Features]] | [[Category:Features]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:51, 19 July 2019
About smart contracts, the basis of conditional payments ("smart payments"), Obyte's killer feature. And "the competition". Not too technical. Compare to Prosaic contracts, and also Autonomous Agents.
Contents
Contracts. Ethereum, right?
Obyte does simple, human-readable contracts to perform simple actions.
Ethereum does complex, programmer-readable contracts to perform complex actions.
No overlap.
But Rootstock?
Rootstock is a centralized smart-contract platform planned to be layered on top of Bitcoin. RSK was just released on Bitcoin testnet.[1]
One post: RSK is EVM on BTC (that is, Ethereum Virtual Machine infrastructure, but linked to and secured by bitcoin's blockchain instead, using sidechains.)
RSK is now supported on Trezor.[2]
Offering smart contracts
When you want to create a new smart contract with a user, your sequence is usually as follows:[3]
- You ask the user to send his payment address (it will be included in the contract)
- You define a new contract using the user's address and your address as parties of the contract
- You pay your share to the contract
- At the same time, you send a specially formatted payment request (different from the payment request above) to the user to request his share. You start waiting for the user's payment
- The user views the contract definition in his wallet and agrees to pay
- You receive the payment notification and wait for it to get confirmed
- After the payment is confirmed, the contract is fully funded.
See wiki Oracle article for examples and videos.
Recovering smart contracts
The contract is hidden once it is emptied but it still exists. To unhide it, you can send any coins, even 1 byte, to the contract address.
External links
References
- ↑ https://www.reddit.com/r/Bitcoin/comments/6e7mdz/rsk_testnet_is_open/?st=j3bxt1g7&sh=63cbb552 Reddit thread 2017-05-30
- ↑ http://gk2.sk/how-to-use-trezor-with-rootstock-rsk-using-myetherwallet Online article 2017-05-30
- ↑ https://github.com/byteball/byteballcore/wiki/Writing-chatbots-for-Byteball Github: Writing chatbots for [Obyte]